It is a painless, in-clinic ultrasound and blood procedure, an easy screening test that a pregnant woman can do and go back to her normal routine after the procedure. This test will rule out birth defects like neural tube, chromosomal abnormality such as trisomy 13, 18, 21, as well as the risk for pregnancy complications detailing the following:
- Risk for fetal growth restriction before 37 weeks
- Risk for pre-eclampsia before 34 weeks
- Risk for pre-eclampsia before 37 weeks
- Risk for pre-eclampsia before 42 weeks
Every pregnant patient should be offered this kind of test regardless of her age. This screening consists of
TWO PARTS:
- BLOOD TEST
This is done ideally during 11 to 12 weeks of pregnancy. This is a screening test for an early detection of aneuploidy pregnancy. This screening is done by the combination of two biochemical markers which are the free Beta HCG and Pregnancy Associated Plasma Protein (PAPP-A). The patient is requested to set an appointment early in the morning since blood samples are referred to an outsource laboratory in Germany.
Be reminded that the level of these results are correlated with the NT scan to calculate the risk of aneuploidy
- NT SCAN/ULTRASOUND
This is ideally performed from the start of 11 weeks to 14 weeks of pregnancy.
Dr. Leila Soudah has been a licensed sonographer and has a certificate of competence in performing the first trimester screening under both the English and German Fetal Medicine Foundation since 2004. This enables her to perform this test and to calculate the risk of abnormality for your baby. Dr. Leila is listed as a sonographer with good audit results under FMF England.
The Scan/Ultrasound demonstrates the following FIRST TRIMESTER MARKER:
Nuchal Translucency
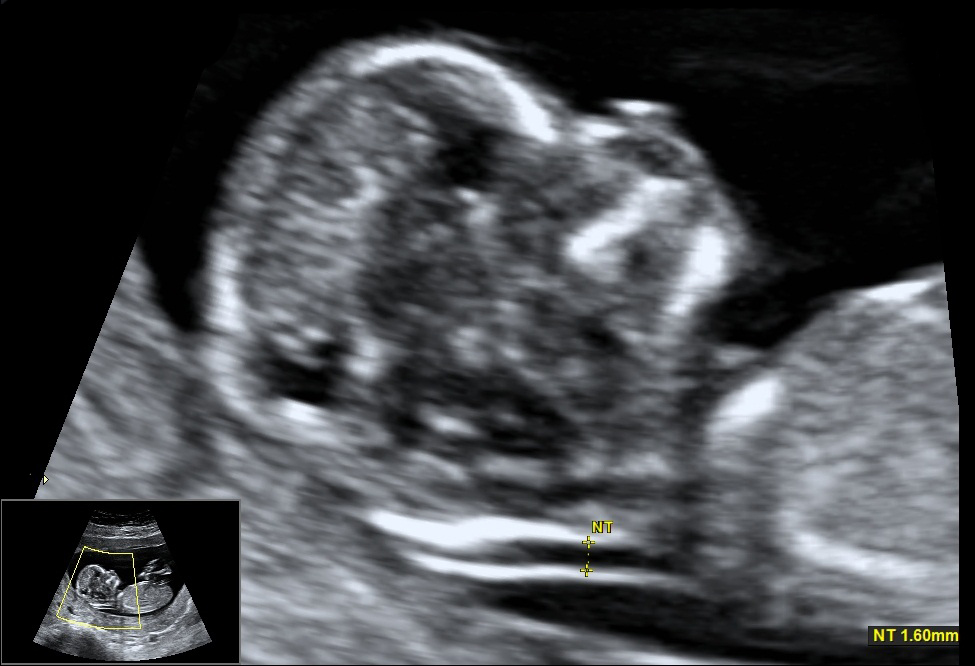
A nuchal translucency ultrasound measures the collection of fluid under the skin behind the fetal neck. NT thickness could increase for a fetus with chromosomal abnormalities, cardiac defects and other genetic syndromes. In correlation with the maternal serum free Beta HCG and PAPP-A provides an effective method for early screening for trisomy 13, 18, 21.
The combination of Nuchal translucency and maternal serum free Beta HCG and PAPP-A increases detection up to 90%. There is now evidence that the detection rate can increase to about 95% and the false positive rate can be reduced to 2.5 % by also examining the following markers:
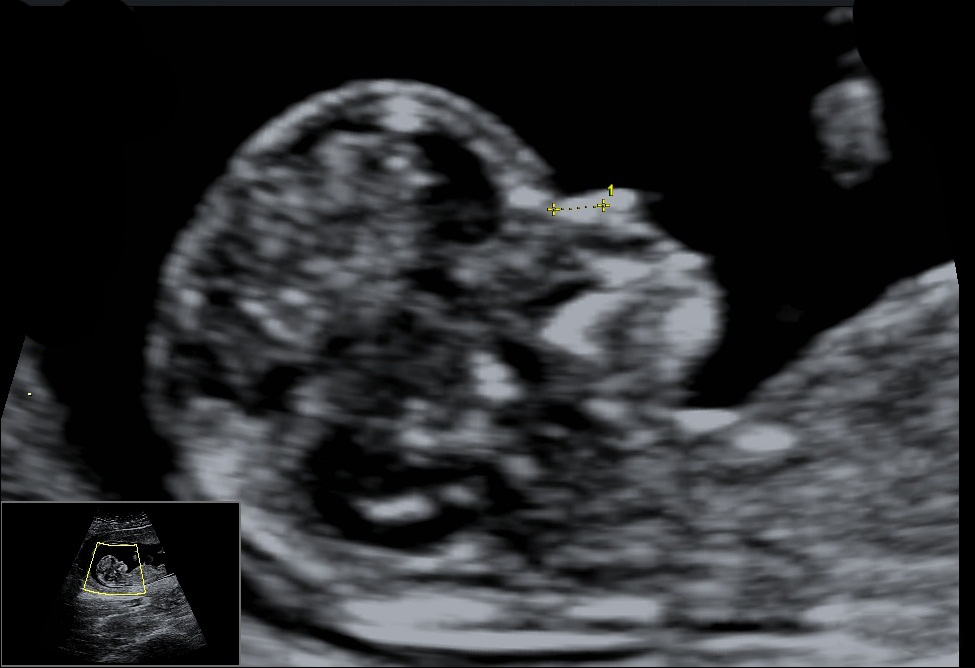
- Nasal Bone: These are two oblique bones, placed side by side at the middle and upper part of the face and form by a junction in "the bridge" of the nose. For fetuses with trisomy 21 and other chromosomal abnormalities, the nasal bone is hypo plastic or not visible at 11-13 weeks of gestation.
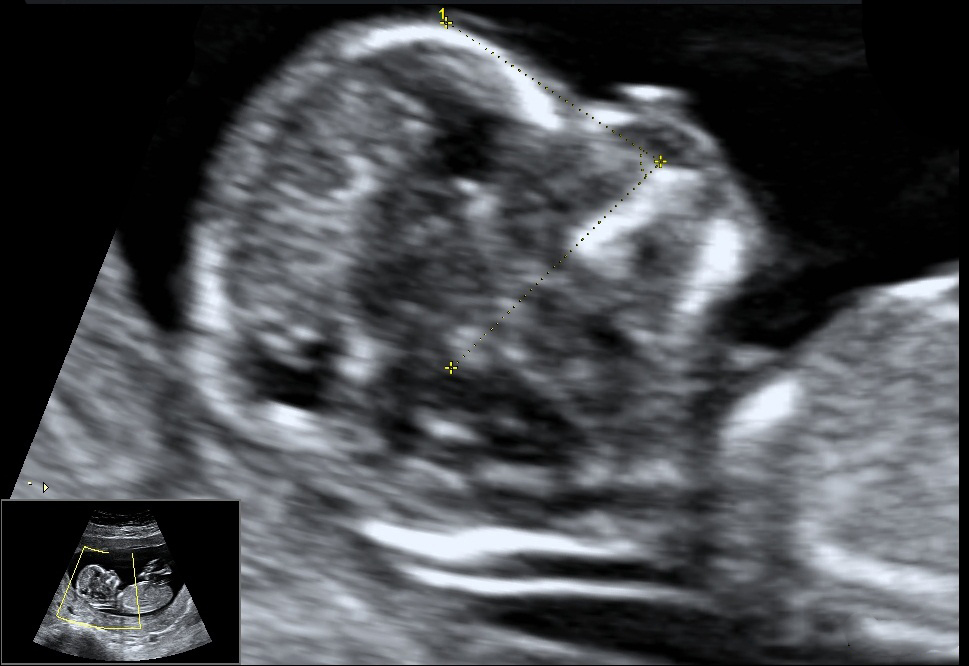
- Facial Angle: It is the wide angle in a line drawn over the palate and between the maxilla and the forehead. Recent studies suggest that fetuses with trisomy 21 have a flat profile because the maxilla (upper jaw) is small and set back.
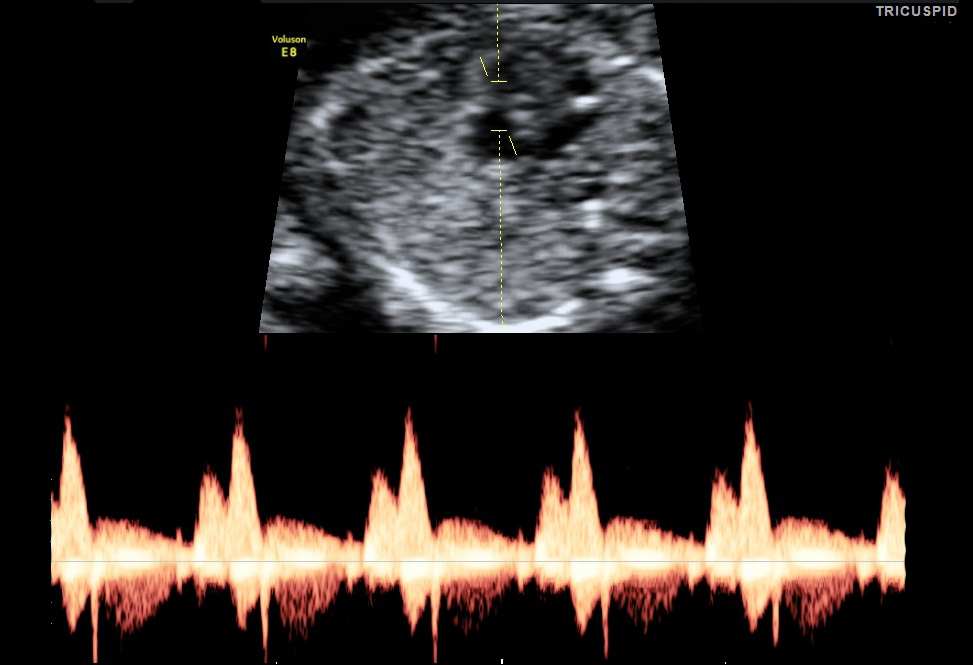
- Tricuspid Valve: Flow of blood between right atrium to right ventricle. This is one of the markers that contribute in the screening for both major cardiac defects.
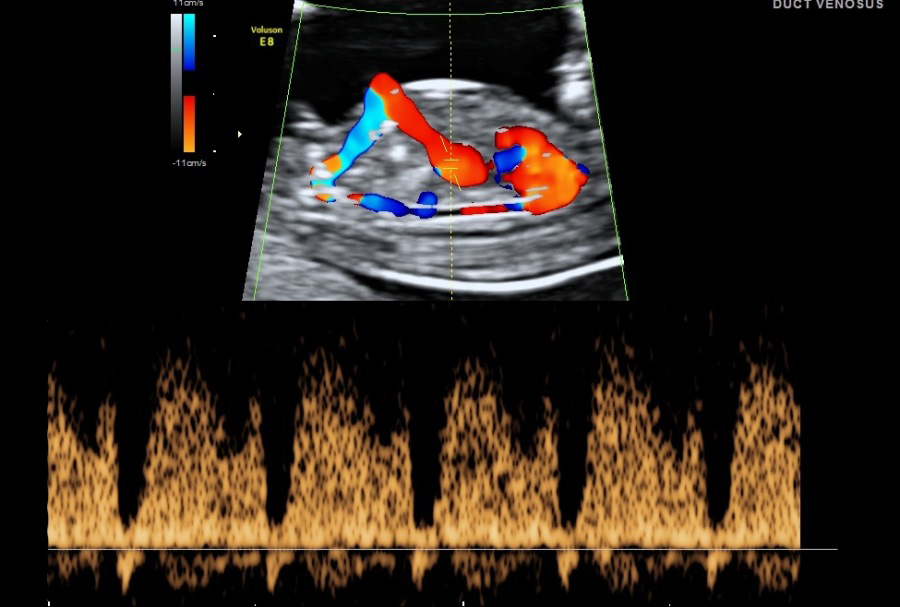
- Ductus Venosus: Blood flow of the umbilical vein directly to the fetal heart. It is part of the fetal circulation. Presence of normal flow will reduce the risk for trisomy 21 and cardiac abnormalities and the presence of reversed A- wave will increase the risk.
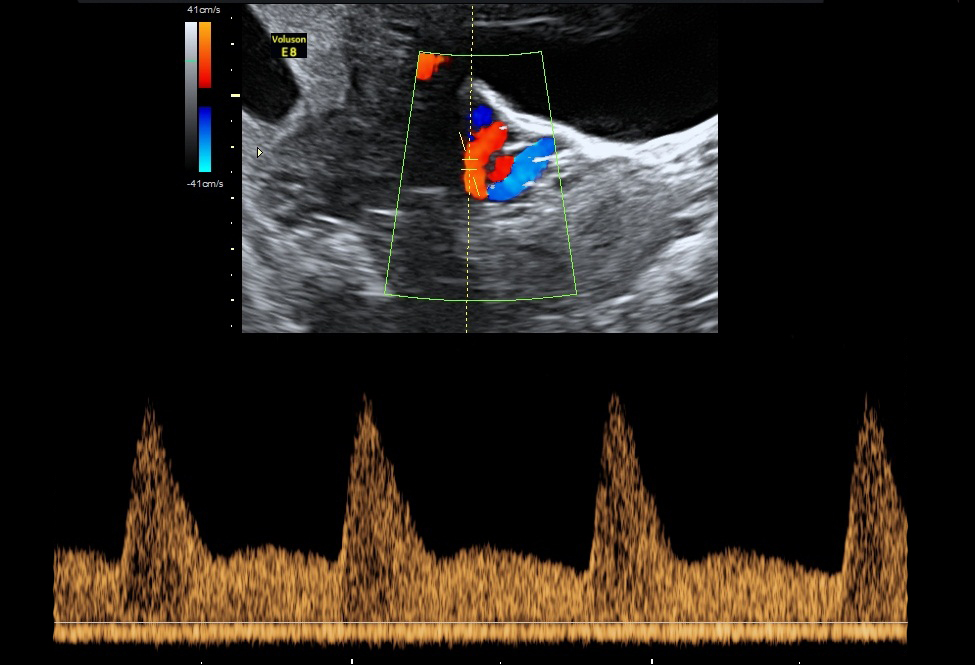
- Uterine Artery PI: It is the two arteries both left and right that supplies blood to the uterus in females. By using maternal history, as well as the uterine artery blood flow and the blood pressure from both arms, we can calculate the risk for complications that may arise during the pregnancy. Some of these complications include pre-eclampsia and hypertension.
Harmony Test
The Harmony Test is a non-invasive method for the detection of fetal trisomies in an unborn child, based on the analysis of genetic material (fetal DNA) that circulates in the mothers' blood.
It is an early and reliable prenatal screening test for the most common chromosomal disorders. It can be performed using the mother’s blood after completion of the 10th week of gestation.
- TRISOMY 21
Trisomy 21 is due to an extra chromosome 21 and is the most common trisomy at the time of birth. Trisomy 21, also known as Down syndrome, is associated with mild to moderate intellectual disabilities, which may also lead to digestive disease and congenital heart defects.
- TRISOMY 18
Trisomy 18 is due to an extra chromosome 18. Trisomy 18, also called Edwards syndrome, is associated with a high rate of miscarriage. Infants born with trisomy 18 often have congenital heart defects as well as various other medical conditions, shortening their lifespan.
- TRISOMY 13
Trisomy 13 is due to an extra chromosome 13. Trisomy 13, also called Patau syndrome, which is associated with a high rate of miscarriage. Infants born with trisomy 13 usually have severe congenital heart defects and other medical conditions. Survival beyond the first year is rare.
Highest Detection Rate
99.7% detection rate for Trisomy 21 in published studies
Lowest False Positive Rate
only 0.06% for Trisomy 21
Women above a certain age have a higher false positive rate for sex chromosome disorders. The Harmony Test false positive rate for trisomy 21 is 0.06%, and is slightly higher for sex chromosome disorders.
High Success Rate
Characterized by a high success rate. According to their own data, 98% of the tests were successful at the first attempt.
Application of the Harmony Test
The test can be applied for all singleton or twin pregnancies, even if the pregnancy is the result of an in-vitro fertilization including egg donation.
In the case of twins, a determination of sex chromosomes disorders (X,Y) and fetal sex is not possible. (REFERENCE: CENATA GmBH)
Amniocentesis
It is an invasive medical procedure used in prenatal diagnosis for chromosomal abnormalities and fetal infections, in which a small amount of amniotic fluid that contains the fetal tissue is aspirated in the amniotic sac surrounding the fetus under the guide of the ultrasound. This procedure is ideally done during weeks 15 to 20 of pregnancy.


 A nuchal translucency ultrasound measures the collection of fluid under the skin behind the fetal neck. NT thickness could increase for a fetus with chromosomal abnormalities, cardiac defects and other genetic syndromes. In correlation with the maternal serum free Beta HCG and PAPP-A provides an effective method for early screening for trisomy 13, 18, 21. The combination of Nuchal translucency and maternal serum free Beta HCG and PAPP-A increases detection up to 90%. There is now evidence that the detection rate can increase to about 95% and the false positive rate can be reduced to 2.5 % by also examining the following markers:
A nuchal translucency ultrasound measures the collection of fluid under the skin behind the fetal neck. NT thickness could increase for a fetus with chromosomal abnormalities, cardiac defects and other genetic syndromes. In correlation with the maternal serum free Beta HCG and PAPP-A provides an effective method for early screening for trisomy 13, 18, 21. The combination of Nuchal translucency and maternal serum free Beta HCG and PAPP-A increases detection up to 90%. There is now evidence that the detection rate can increase to about 95% and the false positive rate can be reduced to 2.5 % by also examining the following markers:




